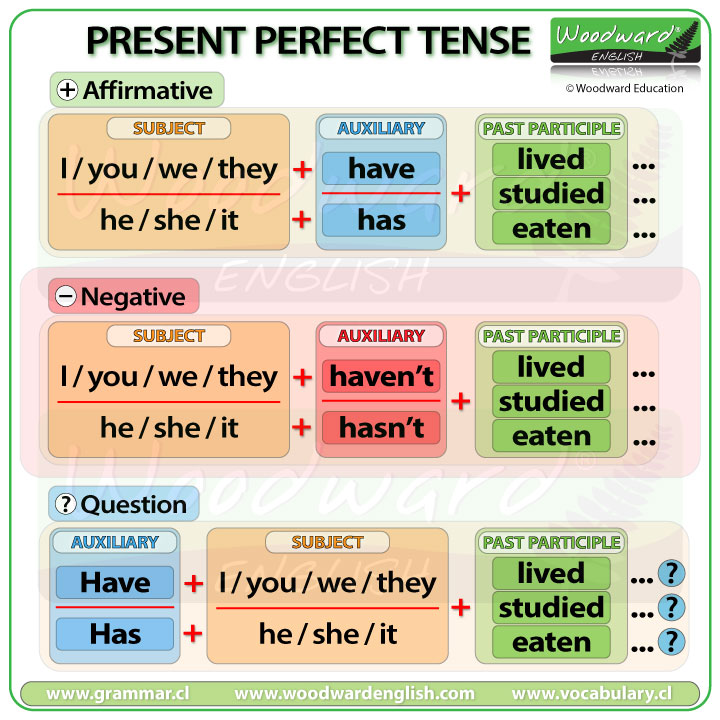
The Present Perfect Tense is formed using the following structure:
Affirmative: Subject + Have / Has + Past Participle
Negative: Subject + Haven't / Hasn't + Past Participle
Question: Have / Has + Subject + Past Participle
The contracted form of the perfect tense is quite common:
We use contractions a lot when we are speaking.
The contraction of the perfect tense in negative form is:
Have not = Haven't
Has not = Hasn't
1. Unspecified point in the past
Compare with the simple past:
2. An action that occurred in the past, but has a result in the present (now)
3. Talking about general experiences (ever, never)
It usually refers to an event happening at some moment in your life.
4. Events that recently occurred (just)
5. Events that have not occurred up to now (yet)
6. Events that occurred before you expected (already)
7. Events that began in the past and haven't changed (for, since)
Here are more details and and examples of when to use the Present Perfect Tense in English

See our new notes about the Present Perfect Tense in English with more summary charts.
If you found this grammar guide about the Present Perfect Tense in English useful, let others know about it.
A variety of English grammar notes and rules including charts and examples for beginner to advanced level students.
Improve your English with our interactive English grammar games. There are many different topics and levels.